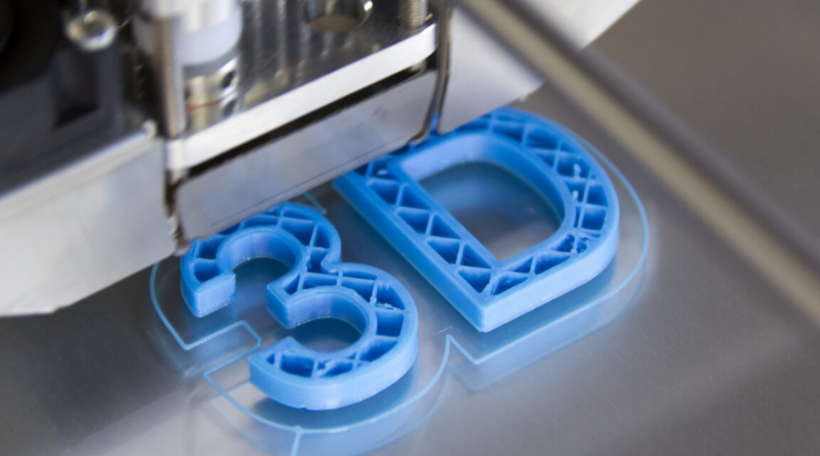
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a transformative technology that is reshaping traditional manufacturing processes and unlocking new possibilities across industries. With its ability to create three-dimensional objects layer by layer, 3D printing offers unprecedented flexibility, customization, and cost-effectiveness. From rapid prototyping to production-grade manufacturing, 3D printing is revolutionizing the way products are designed, developed, and produced. Let’s delve into the world of 3D printing, its key benefits and applications, and its potential to drive innovation in various sectors.
The Basics of 3D Printing
3D printing is a process that builds objects layer by layer using computer-aided design (CAD) models as a blueprint. It starts with a digital design file that is sliced into thin cross-sectional layers. The 3D printer then creates the object by depositing successive layers of material, which can be plastic, metal, ceramic, or even biological materials, depending on the specific technology used. As each layer is added, the material solidifies or fuses together, gradually forming a complete three-dimensional object.
Key Benefits of 3D Printing
- Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows for intricate and complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. It offers design freedom, enabling the creation of highly customized, personalized, and geometrically complex objects.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing significantly speeds up the prototyping process by allowing quick and cost-effective production of physical models. It enables designers and engineers to iterate and test designs more efficiently, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods.
- Cost-Effective Production: 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing methods, especially for low-volume or highly customized production. It eliminates the need for costly tooling and molds, reduces material waste, and enables on-demand manufacturing, thereby lowering production costs and inventory expenses.
- Supply Chain Optimization: 3D printing enables decentralized manufacturing, reducing the reliance on global supply chains. It allows for local production, customization, and just-in-time manufacturing, reducing lead times, transportation costs, and carbon footprints.
- Sustainability: 3D printing has the potential to be more environmentally friendly compared to traditional manufacturing methods. It reduces material waste, as only the required amount of material is used, and enables the recycling and repurposing of materials. Additionally, localized production can help reduce the carbon emissions associated with long-distance shipping.
Applications of 3D Printing
- Prototyping and Product Development: 3D printing is widely used for rapid prototyping in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, consumer products, and healthcare. It allows designers and engineers to quickly visualize and test product designs before moving into large-scale production.
- Customization and Personalization: With 3D printing, products can be easily customized to suit individual needs and preferences. From personalized consumer products to patient-specific medical devices, 3D printing enables mass customization on a scale that was previously unattainable.
- Manufacturing and Production: 3D printing is increasingly being used for production-grade manufacturing, especially for small batch production, spare parts, or products with complex geometries. It offers cost-effective and flexible production solutions, reducing lead times and inventory costs.
- Healthcare and Biotechnology: 3D printing is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling the production of patient-specific medical implants, prosthetics, anatomical models, and even organs and tissues. It has the potential to transform the fields of regenerative medicine and personalized healthcare.
- Education and Research: 3D printing is becoming a valuable tool in education and research, allowing students and researchers to bring concepts to life and explore ideas in a tangible way. It promotes hands-on learning, enhances creativity, and facilitates experimentation across various disciplines.
The Future of 3D Printing
As 3D printing continues to evolve, the technology holds immense potential for further advancements and innovation. Ongoing research and development aim to improve printing speed, increase material options, enhance the precision of printing, and enable the printing of larger objects. Furthermore, advancements in multi-material and multi-color printing, as well as the integration of electronics and sensors, will open up new possibilities for complex, functional, and smart 3D-printed products.
Conclusion
3D printing is transforming traditional manufacturing processes and driving innovation across industries. With its design flexibility, rapid prototyping capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and customization options, 3D printing offers a new dimension of manufacturing possibilities. From rapid prototyping to customized production and healthcare applications, 3D printing is revolutionizing the way we create, design, and manufacture objects. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to witness even more exciting applications and breakthroughs, paving the way for a future where 3D printing plays an increasingly integral role in our lives.